ESCH-R Living Labs
Established in the Erasmus MC and UMC Utrecht
Mission
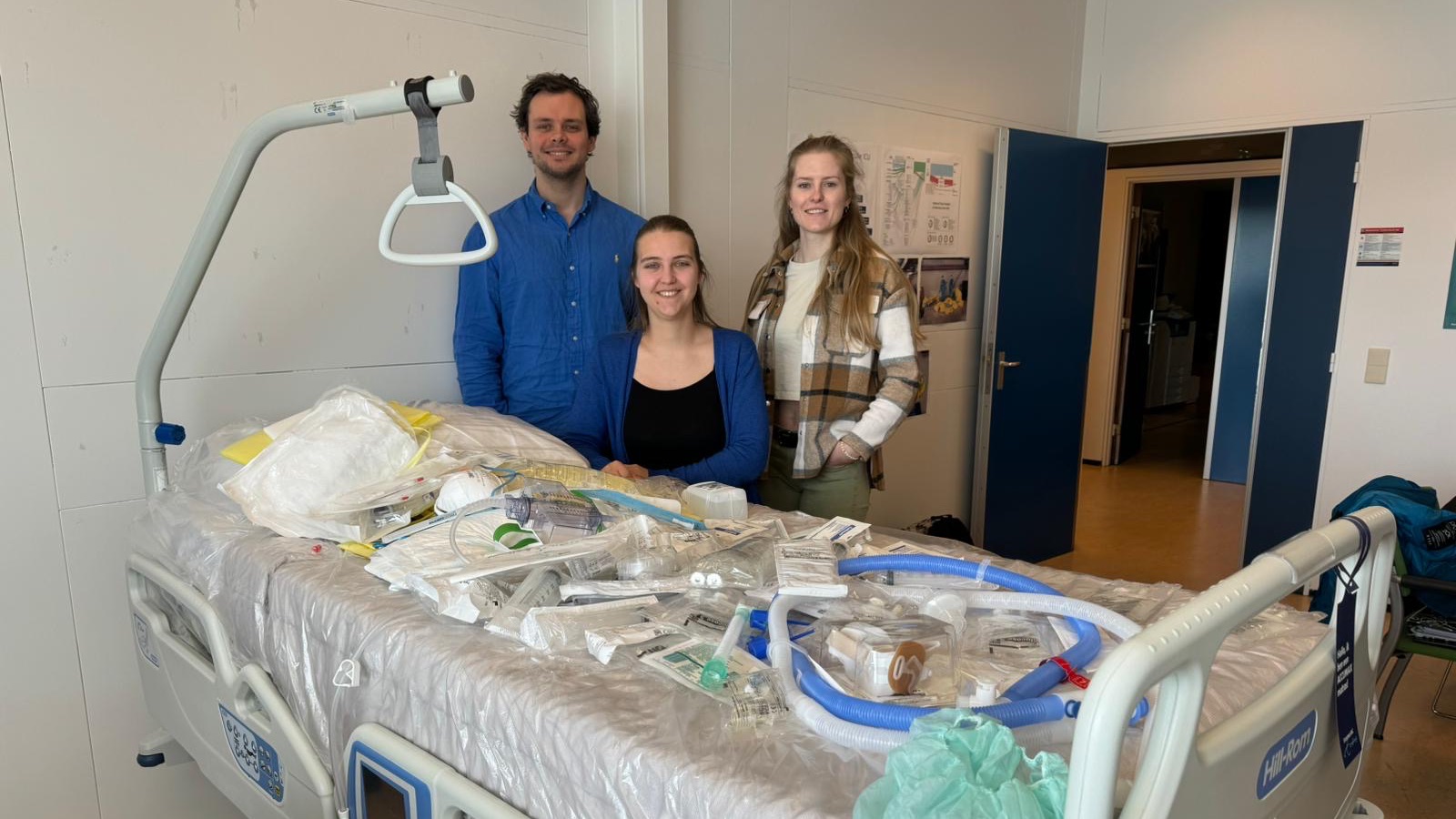
The mission of ESCH-R is to accelerate the adoption of circular interventions in hospitals and, in doing so, reduce the ecological footprint of the healthcare sector in terms of CO₂ emissions, material consumption, and waste production. The overarching research question is therefore: “How can hospitals move away from single-use medical consumables and transition towards circularity?”
To explore this, the ESCH-R research project has also established two Living Labs: one at Erasmus MC and one at UMC Utrecht. These hospitals host the ESCH-R Living Labs, where existing medical devices and new interventions are tested, developed, and validated based on the 10-Rs framework for circularity (Refuse, Rethink, Reduce, Re-use, Repair, Refurbish, Remanufacture, Repurpose, Recycle, and Recover).
Research focus
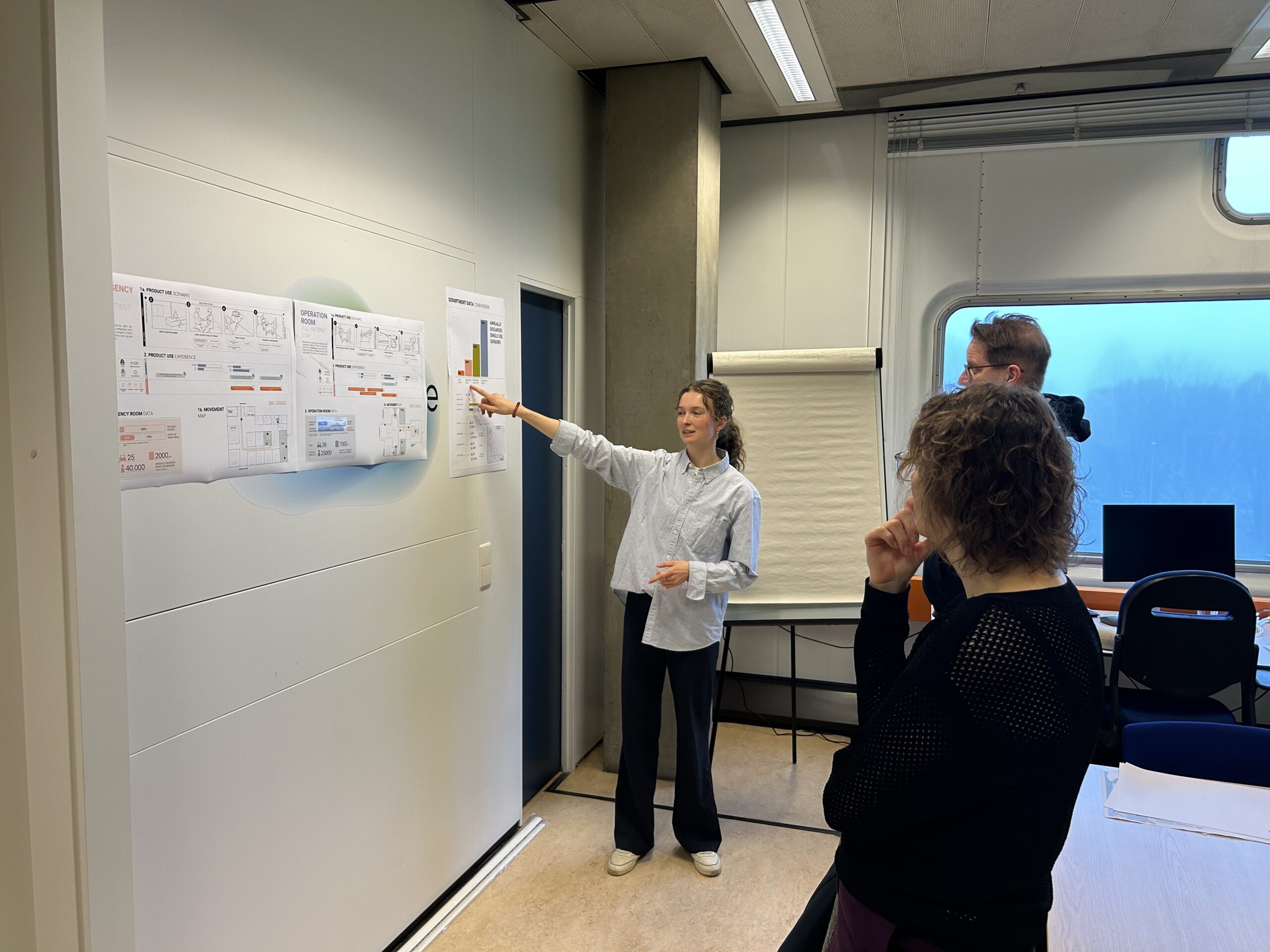
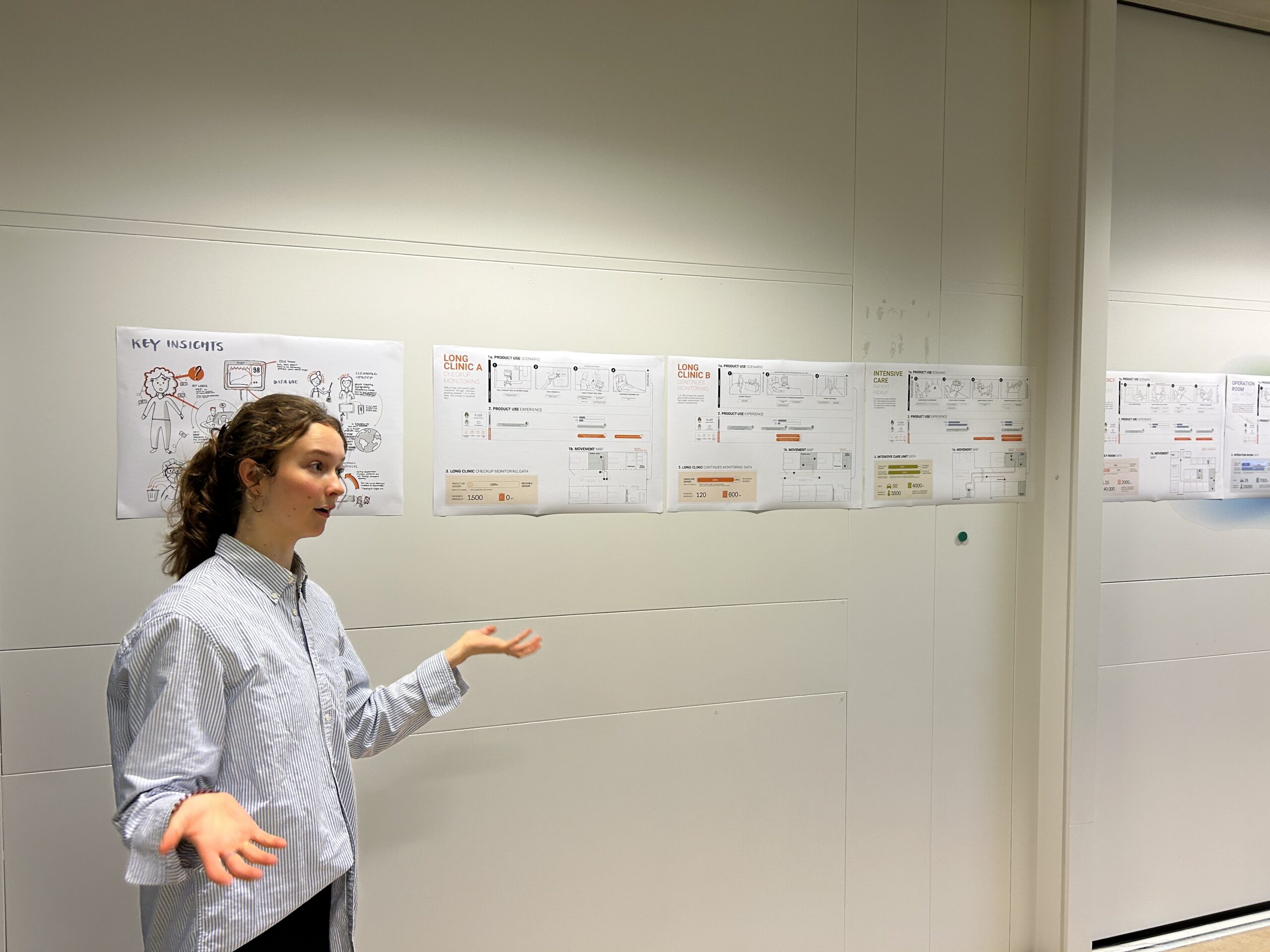
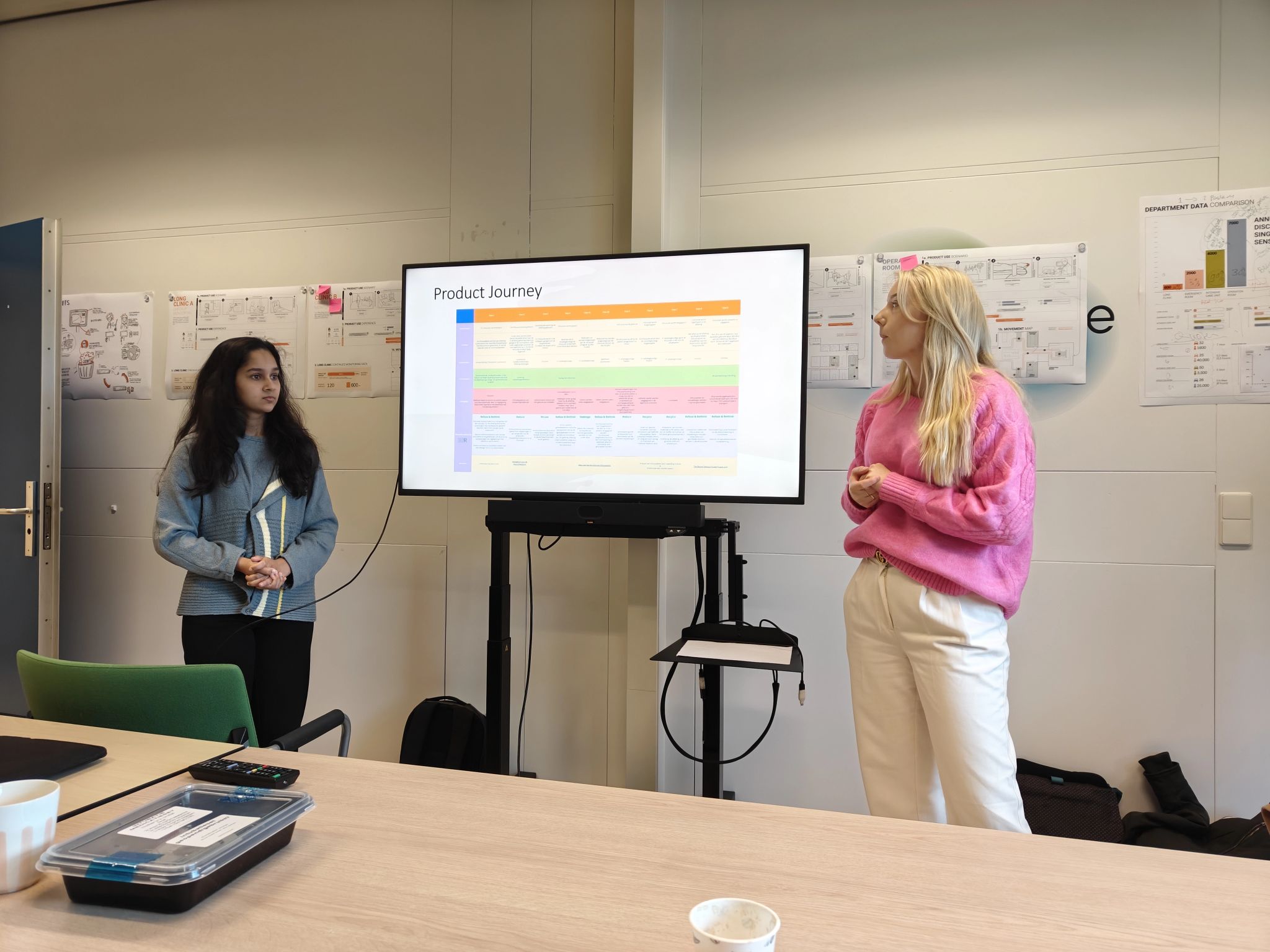
The focus within ESCH-R is to identify key environmental impact hotspots related to medical consumables used in currently six departments: the intensive care units and intervention cardiology and obstetric departments of the Erasmus MC, and the ophthalmology, urology and nephrology departments in UMC Utrecht.
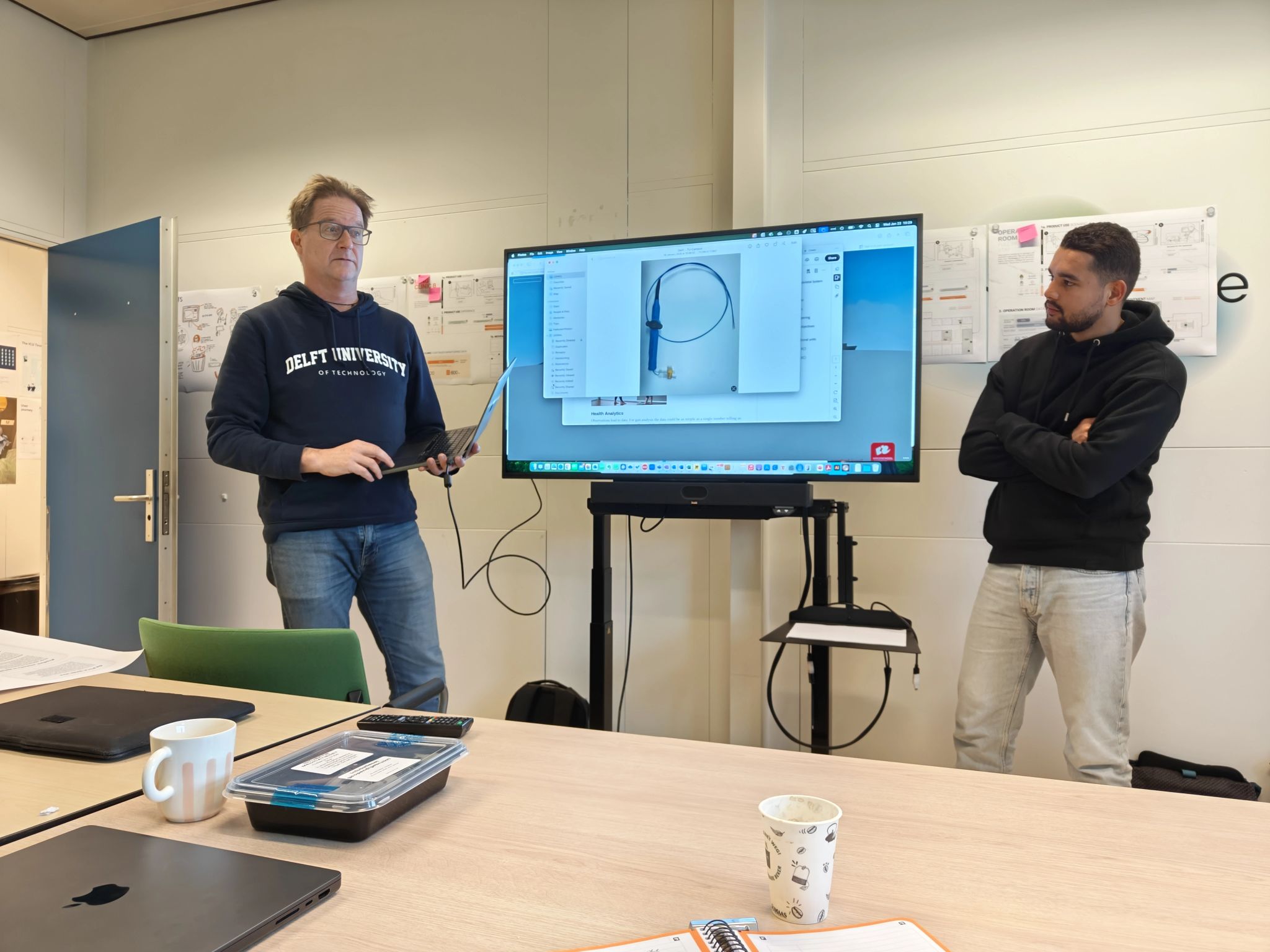
During this process we asses for example questions like ‘How can we make an existing medical device like the Pulse Oxi meter more circular as the single use varieties create a lot of waste?’ and ‘Can single-use dialysis bags be made from an alternative type of plastic to improve its recyclability?’
Collaboration
Within the overall project (and so also in the Living Labs), ESCH-R researchers, PhD candidates, and students collaborate closely with industrial partners, including plastic manufacturers (Wittenburg Group), medical device developers and suppliers (Medtronic, Philips, and DORC), and waste management companies (Saba and PreZero). Together, they review existing products and develop new circular solutions based on the 10-Rs framework.
The ESCH-R Living Labs serve as hubs for co-creation and co-validation, bringing together stakeholders from across the entire value chain—from manufacturers to waste processors—to develop and implement circular solutions.
Over the course of the ESCH-R project, a total of 12 case studies will be undertaken to drive the transition towards a more circular healthcare system.







